CV – Research – Lab members – Publications
 Dr. Ginny G. Farías
Dr. Ginny G. Farías
Cell Biology, Neurobiology and Biophysics,
Faculty of Science, Utrecht University
Kruytgebouw, room Z509
Padualaan 8, 3584 CH Utrecht
The Netherlands
Email: g.c.fariasgaldames@uu.nl
Curriculum Vitae
Ginny G. Farías studied Biology at the P. Catholic University of Chile in Chile, where she also obtained her PhD in Cellular and Molecular Biology (2009). After her training in molecular biology of neurons and neurodegeneration with Dr. Nibaldo C. Inestrosa, she performed a postdoctoral stay with Dr. Juan S. Bonifacino at the National Institutes of health (NIH), Maryland, USA (2010-2016). Here, she used high spatio-temporal resolution imaging in conjunction with genetic engineering approaches, to study polarized sorting of proteins in neurons. In 2016, she joined the Division of Cell Biology, Department of Biology at Utrecht University. Here, she has been developing new tools and strategies to study organelle dynamics and their contribution to neuronal polarity. In 2018, she started her own independent group with a NWO-VIDI grant and in 2020 she received a ERC-starting grant. In 2024, she was interviewed by Journal of Cell Science as a scientist to watch.
Research summary
Our goal is to understand the molecular mechanisms by which organelles are organized within the neuron, and how this organelle organization and networking contributes to protein sorting, and neuronal development and function. Organelle disorganization has been shown to be strongly involved in several neurological diseases; however, it is unknown if the altered organelle organization is the cause or just a consequence of impaired neuronal function. By deciphering the basic molecular mechanisms underlying organelle organization and inter-organelle communication, we can better understand how they contribute to neuronal function.
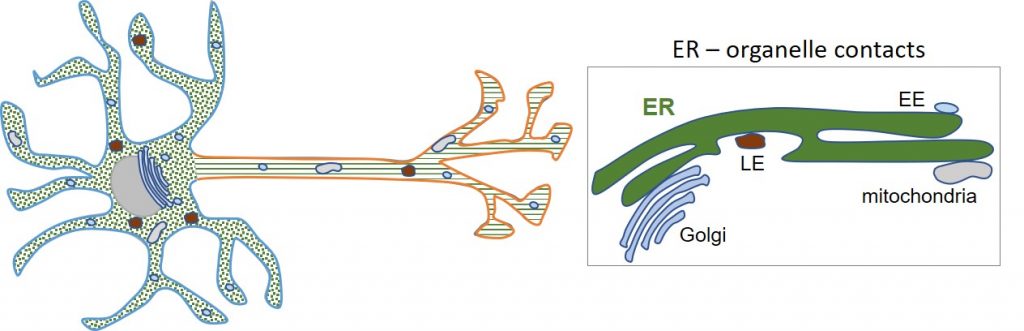
One of the main research lines of our lab is studying the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This is one of the largest and most multifunctional organelles in cells and consists of an interconnected network of two different shapes: ER cisternae and ER tubules. In neurons, ER tubules are distributed along the somatodendritic and axonal domains, while ER cisternae are restricted to the somatodendritic domain. The ER network forms contacts with several other organelles and the cytoskeleton.
We currently investigate: i) the machineries responsible for the organization and dynamics of the segregated ER in neurons; ii) the role of local ER organization in organelle and cytoskeleton dynamics; and iii) the contribution of ER networking to neuronal polarity. We also investigate i) mechanisms of polarized sorting of proteins; ii) regulation of local mRNA translation; iii) biogenesis of organelles in neurons.
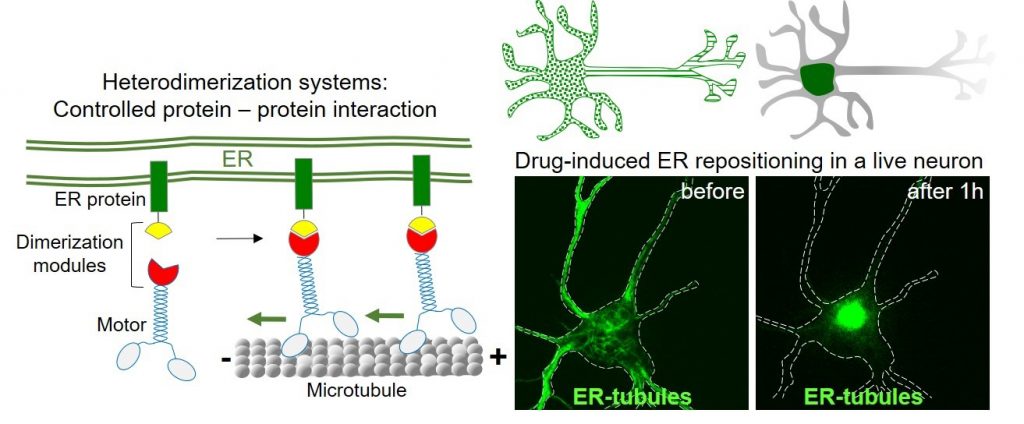
We use primary cultures of rat neurons as a model system. In these neurons, we use live-cell imaging of fluorescently tagged proteins in combination with photobleaching and photoactivation techniques to study organelle dynamics and protein sorting. By using and developing innovative genetic engineering tools called heterodimerization systems, we study organelle contacts and their local roles in neuronal development and function.
Lab members
| PhD students: | |
| Mai Dan Nguyen | t.m.d.nguyen@uu.nl |
| Chun Hei Li | c.h.li@uu.nl |
| Ha Nguyen | t.h.h.nguyen@uu.nl |
| Derk Draper | d.b.h.draper@uu.nl |
| Noortje Kersten | n.kersten@uu.nl |
| Meizhen Xie | m.xie1@uu.nl |
| Semanti Das | s.das@uu.nl |
| Ayse Reyyan Kutan Basci | a.r.kutanbasci@uu.nl |
| Post-Docs: | |
| Maarten Bebelman | m.p.bebelman@uu.nl |
| Paolo Sanza (shared with UMCU) | p.sanza@umcutrecht.nl |
| Master Students: | |
| Stela Papadaki | s.papadaki@students.uu.nl |
Publications
2024
Li CH, Kersten N, Özkan N, Koppers M, Post H, Altelaar M, Farias GG, Spatiotemporal proteomics reveals the biosynthetic lysosomal membrane protein interactome in neurons. Nat Commun (in press) 2025, doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55052-w
Koppers M, Özkan N, Nguyen HH, Jurriens D, McCaughey J, Nguyen DTM, Li CH, Stucchi R, Altelaar M, MacGillavry HD, Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC, Farías GG. Axonal endoplasmic reticulum tubules control local translation via P180/RRBP1-mediated ribosome interactions. Dev Cell. 2024 Aug 19;59(16):2053-2068.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.05.005. Epub 2024 May 29.PMID: 38815583.
Nguyen DTM, Koppers M, Farías GG. Endoplasmic reticulum – condensate interactions in protein synthesis and secretion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024 Jun;88:102357. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102357. Epub 2024 Apr 15. PMID: 38626704.
2023
Kersten N, Farías GG. A voyage from the ER: spatiotemporal insights into polarized protein secretion in neurons. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 22;11:1333738. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1333738. PMID: 38188013.
2022
van Leeuwen W*, Nguyen DTM*, Grond R, Veenendaal T, Rabouille C#, Farías GG#. Stress-induced phase separation of ERES components into Sec bodies precedes ER exit inhibition in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci., 2022. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260294.
2021
Nguyen HH, Farías GG. Moving the ER tip by tip. Dev Cell., 2021, 56:3305-3306
Özkan N, Koppers N, Soest I, Harten A, Liv N, Klumperman J, Hoogenraad CC, Farías GG. ER – lysosome contacts at a pre-axonal region regulate axonal lysosome availability. Nat Commun., 2021, 12:4493.
Koppers M, Farías GG. Organelle distribution in neurons: Logistics behind polarized transport. Curr. Opin Cell Biol., 2020, 71:46-54.
2020
Koppers M, Özkan N, Farías GG. Complex interactions between membrane-bound organelles, biomolecular condensates and the cytoskeleton. Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2020, 8:618733
2019
Farías GG*, Fréal A, Tortosa E, Stucchi R, Pan X, Portegies S, Will L, Altelaar M, Hoogenraad CC*. Feedback-driven mechanisms between microtubules and the endoplasmic reticulum instruct neuronal polarity. Neuron 2019, 102(1):184-201.
2017
Farías GG, Guardia CM, De Pace R, Britt DJ, Bonifacino JS. BORC/Kinesin-1 ensemble drives polarized transport of lysosomes into the axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017, 114(14): E2955-E2964.
2016
Guardia CM, Farías GG, Jia R, Pu J, Bonifacino JS. BORC functions upstream of kinesins 1 and 3 to coordinate regional movement of lysosomes along different microtubule tracks. Cell Reports 2016, 17(8): 1950-1961.
Guo X*, Farías GG*, Mattera R, Bonifacino JS. Rab5 and its effector FHF contribute to neuronal polarity through dynein-dependent retrieval of somatodendritic proteins from the axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016, 113(36): E 5318-5327. * Equal contribution
Farías GG, Britt DJ, Bonifacino JS. Imaging the polarized sorting of proteins from the Golgi complex in live neurons. Methods Mol Biol. 2016, 1496:13-30.
Britt DJ, Farías GG, Guardia CM, Bonifacino JS. Mechanisms of polarized organelle distribution in neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10:88.
2015
Farías GG, Guardia CM, Britt DJ, Guo X, Bonifacino JS. Sorting of dendritic and axonal vesicles at the pre-axonal exclusion zone. Cell Reports 2015, 13(6): 1221-1232.
Jain S, Farías GG, Bonifacino JS. Polarized sorting of the copper transporter ATP7B in neurons mediated by recognition of a dileucine signal by AP-1. Mol Biol Cell 2015, 26(2): 218-228.
2014
Mattera R*, Farías GG*, Mardones GA, Bonifacino JS. Co-assembly of viral envelope glycoproteins regulates their polarized sorting in neurons. PloS Pathog. 2014, 10(5): e1004107. * Equal contribution
Farías GG, Gershlick DC, Bonifacino JS. Going forward with retromer. Dev Cell. 2014, 29(1): 3-4.
2013
Inestrosa NC, Godoy JA, Vargas JY, Arrazola MS, Rios JA, Carvajal FJ, Serrano FG, Farías GG. Nicotine prevents synaptic impairment induced by amyloid-β oligomers through α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation. Neuromolecular Med. 2013, 15(3): 549-569.
Ren X, Farías GG, Canagarajah BJ, Bonifacino JS, Hurley JH. Structural basis for recruitment and activation of the AP-1 clathrin adaptor complex by Arf1. Cell 2013, 152(4): 755-767.
2012
Farías GG, Cuitino L, Guo X, Ren X, Jarnik M, Mattera R, Bonifacino JS. Signal-mediated, AP-1/clathrin-dependent sorting of transmembrane receptors to the somatodendritic domain of hippocampal neurons. Neuron 2012, 75(5): 810-823.
Prabhu Y, Burgos PV, Schindler C, Farías GG, Magadán JG, Bonifacino JS. Adaptor protein 2-mediated endocytosis of the β-secretase BACE1 is dispensable for amyloid precursor protein processing. Mol Biol Cell. 2012, 23(12): 2339-2351.
Varela-Nallar L, Parodi J, Farías GG, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-5a is a synaptogenic factor with neuroprotective properties against Aβ toxicity. Neurodegener Dis. 2012, 10(1-4): 23-26.
2010-2004
2010
Cuitino L, Godoy JA, Farías GG, Couve A, Bonansco C, Fuenzalida M, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-5a modulates recycling of functional GABAA receptors on hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 2010, 30(25): 8411-8420.
Cerpa W, Farías GG, Fuenzalida M, Bonansco C, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-5a occludes Aβ oligomer-induced depression of glutamatergic transmisión in CA1 pyramidal neurons from hippocampal slices. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5:3.
Farías GG, Godoy JA, Varela-Nallar L, Inestrosa NC. Wnt Signaling modulates pre- and postsynaptic maturation. Therapeutic considerations. Develop Dynamics 2010, 239(1): 94-101.
2009
Farías GG, Alfaro IE, Grabowski CP, Godoy JA, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-5a/ JNK signaling promotes the clustering of PSD-95 in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 2009, 284(23): 15857-15866.
2008
Cerpa W, Godoy JA, Alfaro I, Farías GG, Metcalfe MJ, Fuentealba R, Bonansco C, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-7a modulates the synaptic vesicle cycle and synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283(9): 5918-5927.
2007
Farías GG, Valles AS, Colombres M, Godoy JA, Toledo EM, Lukas RJ, Barrantes FJ, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-7a induces presynaptic colocalization of α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and adenomatous polyposis coli in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 2007, 27(20): 5313-5325.
2005
Farías GG, Godoy A, Vázquez MC, Adani R, Meshulam H, Jesús Avila, Amitai G, Inestrosa NC. The anti-inflammatory and cholinesterase inhibitor bifunctional compound IBU-PO protects from β-amyloid neurotoxicity by acting on Wnt signaling components. Neurob. Dis. 2005, 18(1): 176-183.
2004
Fuentealba RA, Farías G, Scheu J, Bronfman M, Marzolo MP, Inestrosa NC. Signal transduction during amyloid β-peptide neurotoxicity: role in Alzheimer disease. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004, 47(1-3): 275-289.
Farías GG, Godoy A, Hernández F, Avila J, Fisher A, Inestrosa NC. M1 muscarinic receptor activation protects neurons from β-amyloid toxicity. A role for Wnt signaling pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 17(2): 337-348.